Air Cooled Condensers
Air cooled condensers (ACCs) are commonly found in power plants and transfer heat from the steam that exits a steam turbine into the surrounding air, without consuming water. This is achieved by passing air over finned tube bundles arranged in either an A-frame or V-frame configuration – also known as forced draft and induced draft respectively.
As a market leader, IWC supplies a competitive range of air-cooled condensers around the globe. Our new range of ACC’s are designed to have a lower environmental impact by targeting a reduction in water use, energy use and carbon emissions.
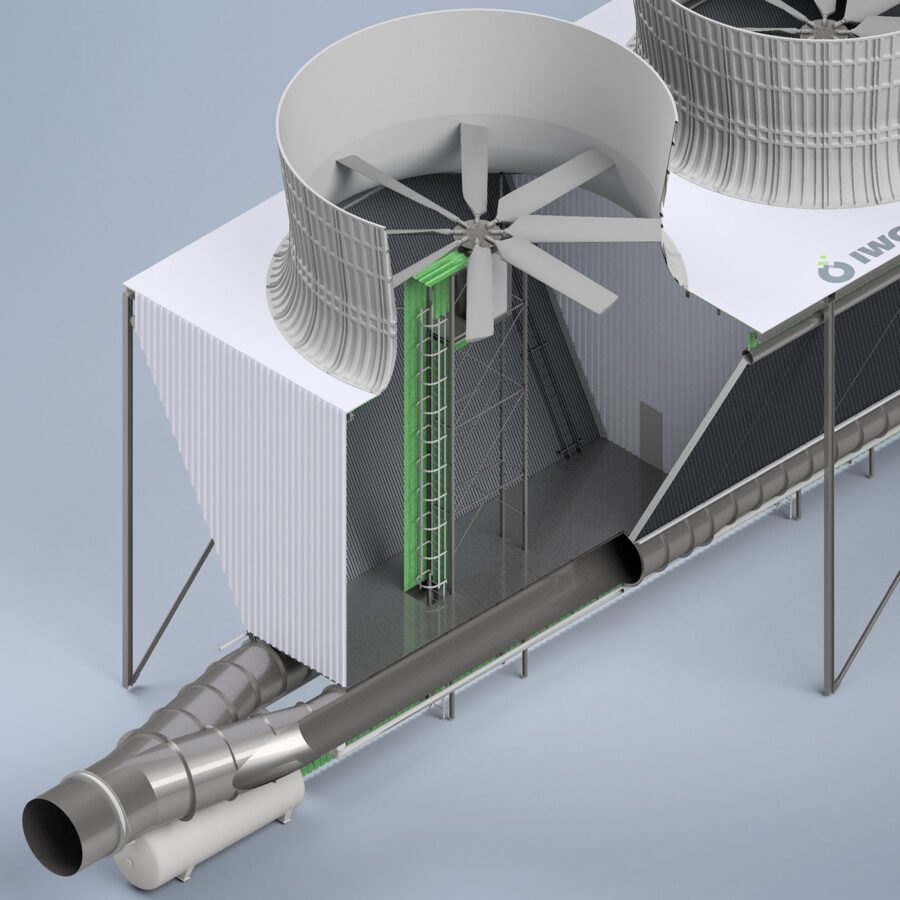
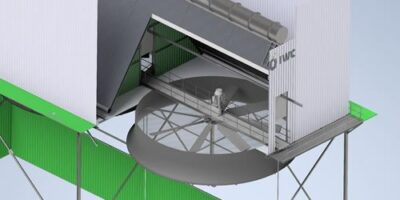
Air Cooled Condenser

Induced Draft
Air Cooled Condenser
The Induced Draft Air Cooled Condenser uses a combination of forced air and natural draft to remove heat from the system, allowing for efficient cooling without the need for water or other cooling fluids.
Movement of the cooling air across the finned tubes is achieved by electrically driven axial flow fans that are installed above the tube bundles in the warm outlet air.
Advantages of Induced Draft unit over Forced Draft
- Improved constructability and shorter erection period.
- Reduced negative performance impact due to wind.
- Improved condensate and air extraction pipe routing.
- Mechanicals have own support structure on foundation plinths.
- Less structural steel.
- Improved air extraction.
Air Cooled Condenser
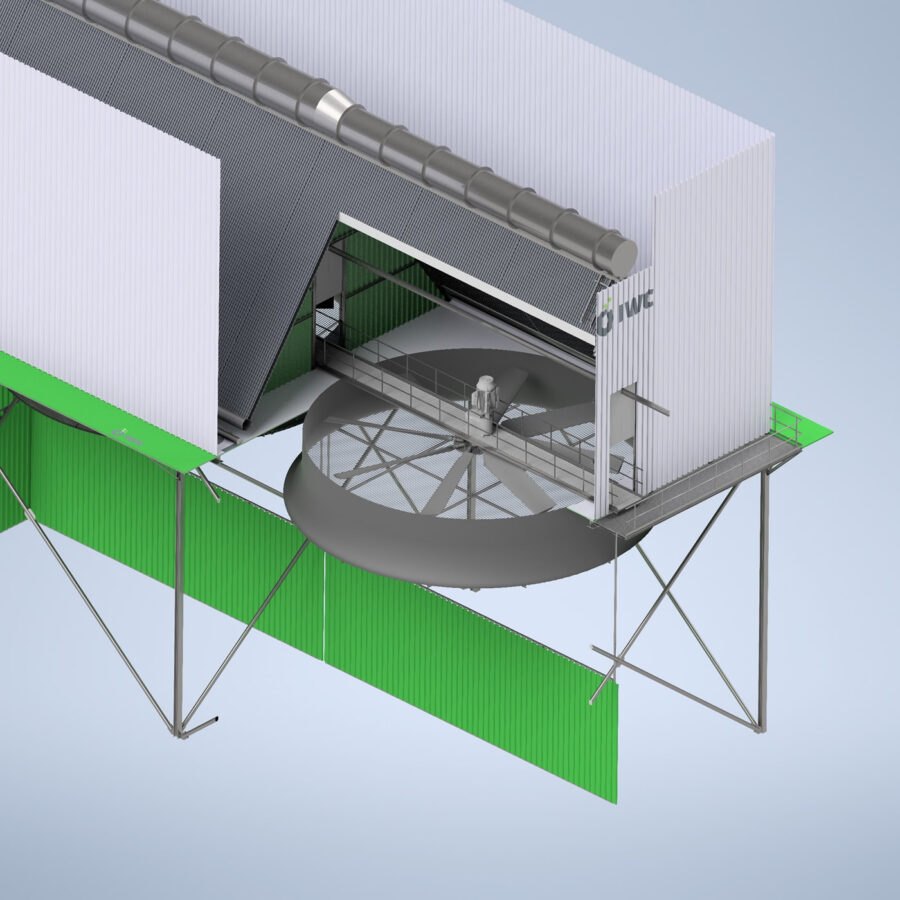
Forced Draft
Air Cooled Condenser
A forced draft air cooled condenser is a type of heat exchanger used in various industrial applications to remove heat from a process fluid by transferring it to the surrounding air.
Movement of the cooling air across the finned tubes is achieved by electrically driven axial flow fans that are installed in the cooler inlet air, below the finned tubes.
Advantages of Forced Draft unit over Induced Draft
- Easy access to fan mechanicals for maintenance and repairs.
- No auxiliary cooling required for motors and gearboxes.
- Condensate tanks can be at higher elevations for improved pump NPSH.